16 KiB
LoopBack Definition Language Guide
LoopBack Definition Language (LDL) is simple DSL to define data models in JavaScript or plain JSON. With LoopBack, we often start with a model definition which describes the structure and types of data. The model establishes common knowledge of data in LoopBack.
Describing a simple model
Let's start with a simple example in plain JSON.
{
"id": "number",
"firstName": "string",
"lastName": "string"
}
The model simply defines a user model that consists of three properties:
- id - The user id. It's a number.
- firstName - The first name. It's a string.
- lastName - The last name. It's a string.
Each key in the JSON object defines a property in our model which will be cast
to its associated type. The simplest form of a property definition is
propertyName: type. The key is the name of the property and the value is the
type of the property. We'll cover more advanced form later in this guide.
LDL supports a list of built-in types, including the basic types from JSON:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
Note: The type name is case-insensitive, i.e., either "Number" or "number" can be used.
The same model can also be described in JavaScript code:
var UserDefinition = {
id: Number,
firstName: String,
lastName: String
}
As we can see, the JavaScript version is less verbose as it doesn't require
quotes for property names. The types are described using JavaScript constructors,
for example, Number for "Number". String literals are also supported.
Now we have the definition of a model, how do we use it in LoopBack Node.js code? It's easy, LoopBack will build a JavaScript constructor (or class) for you.
Creating a model constructor
LDL compiles the model definition into a JavaScript constructor using
ModelBuilder.define APIs. ModelBuilder is the basic factory to create model
constructors.
ModelBuilder.define() method takes the following arguments:
- name: The model name
- properties: An object of property definitions
- options: An object of options, optional
Here is an example,
var ModelBuilder = require('loopback-datasource-juggler').ModelBuilder;
// Create an instance of the ModelBuilder
var modelBuilder = new ModelBuilder();
// Describe the user model
var UserDefinition = {
id: Number,
firstName: String,
lastName: String
}
// Compile the user model definition into a JavaScript constructor
var User = modelBuilder.define('User', UserDefinition);
// Create a new instance of User
var user = new User({id: 1, firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith'});
console.log(user.id); // 1
console.log(user.firstName); // 'John'
console.log(user.lastName); // 'Smith'
That's it. Now you have a User constructor representing the user model.
At this point, the constructor only has a set of accessors to model properties. No behaviors have been introduced yet.
Adding logic to a model
Models describe the shape of data. To leverage the data, we'll add logic to the model for various purposes, such as:
- Interact with the data store for CRUD
- Add behavior around a model instance
- Add service operations using the model as the context
There are a few ways to add methods to a model constructor:
Create the model constructor from a data source
A LoopBack data source injects methods on the model.
var DataSource = require('loopback-datasource-juggler').DataSource;
var ds = new DataSource('memory');
// Compile the user model definition into a JavaScript constructor
var User = ds.define('User', UserDefinition);
// Create a new instance of User
User.create({id: 1, firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith'}, function(err, user) {
console.log(user); // The newly created user instance
User.findById(1, function(err, user) {
console.log(user); // The user instance for id 1
user.firstName = 'John1'; // Change the property
user.save(function(err, user) {
console.log(user); // The modified user instance for id 1
});
};
});
Attach the model to a data source
A plain model constructor created from ModelBuilder can be attached a DataSource.
var DataSource = require('loopback-datasource-juggler').DataSource;
var ds = new DataSource('memory');
User.attachTo(ds); // The CRUD methods will be mixed into the User constructor
Manually add methods to the model constructor
Static methods can be added by declaring a function as a member of the model constructor. Within a class method, other class methods can be called using the model as usual.
// Define a static method
User.findByLastName = function(lastName, cb) {
User.find({where: {lastName: lastName}, cb);
};
User.findByLastName('Smith', function(err, users) {
console.log(users); // Print an array of user instances
});
Instance methods can be added to the prototype. Within instance methods, the model instance itself can be referenced with this keyword.
// Define a prototype method
User.prototype.getFullName = function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
};
var user = new User({id: 1, firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith'});
console.log(user.getFullName()); // 'John Smith'
Exploring advanced LDL features
As we mentioned before, a complete model definition is an object with three properties:
- name: The model name
- options: An object of options, optional
- properties: An object of property definitions
Model level options
There are a set of options to control the model definition.
-
strict:
- true: Only properties defined in the model are accepted. Use this mode if you want to make sure only predefined properties are accepted.
- false: The model will be an open model. All properties are accepted, including the ones that not predefined with the model. This mode is useful if the mobile application just wants to store free form JSON data to a schema-less database such as MongoDB.
- undefined: Default to false unless the data source is backed by a relational database such as Oracle or MySQL.
-
idInjection:
- true: An
idproperty will be added to the model automatically - false: No
idproperty will be added to the model
- true: An
-
plural: The plural form of the model name. If not present, it will be derived from the model name following English conventions.
-
Data source specific mappings The model can be decorated with connector-specific options to customize the mapping between the model and the connector. For example, we can define the corresponding schema/table names for Oracle as follows:
{ "name": "Location", "options": { "idInjection": false, "oracle": { "schema": "BLACKPOOL", "table": "LOCATION" } }, ... }
Property definitions
A model consists of a list of properties. The basic example use
propertyName: type to describe a property.
Properties can have options in addition to the type. LDL uses a JSON object to describe such properties, for example:
"id": {"type": "number", "id": true, "doc": "User ID"}
"firstName": {"type": "string", "required": true, "oracle": {"column": "FIRST_NAME", "type": "VARCHAR(32)"}}
Note "id": "number" is a short form of "id": {"type": "number"}.
Data types
LDL supports the following data types.
- String/Text
- Number
- Date
- Boolean
- Buffer/Binary
- Array
- Any/Object/JSON
- GeoPoint
Array types
LDL supports array types as follows:
{emails: [String]}{"emails": ["String"]}{emails: [{type: String, length: 64}]}
Object types
A model often has properties that consist of other properties. For example, the
user model can have an address property
that in turn has properties such as street, city, state, and zipCode.
LDL allows inline declaration of such properties, for example,
var UserModel = {
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
address: {
street: String,
city: String,
state: String,
zipCode: String
},
...
}
The value of the address is the definition of the address type, which can be
also considered as an anonymous model.
If you intend to reuse the address model, we can define it independently and reference it in the user model. For example,
var AddressModel = {
street: String,
city: String,
state: String,
zipCode: String
};
var Address = ds.define('Address', AddressModel);
var UserModel = {
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
address: 'Address', // or address: Address
...
}
var User = ds.define('User', UserModel);
Note: The user model has to reference the Address constructor or the model
name - 'Address'.
ID(s) for a model
A model representing data to be persisted in a database usually has one or more
properties as an id to uniquely identify the model instance. For example, the
user model can have user ids.
By default, if no id properties are defined and the idInjection of the model
options is false, LDL will automatically add an id property to the model as follows:
id: {type: Number, generated: true, id: true}
To explicitly specify a property as id, LDL provides an id property for the
option. The value can be true, false, or a number.
- true: It's an id
- false or any falsey values: It's not an id (default)
- a positive number, such as 1 or 2: It's the index of the composite id
LDL supports the definition of a composite id that has more than one properties. For example,
var InventoryDefinition =
{
productId: {type: String, id: 1},
locationId: {type: String, id: 2},
qty: Number
}
The composite id is (productId, locationId) for an inventory model.
Note: Composite ids are NOT supported as query parameters in REST APIs yet.
Property documentation
- doc: Documentation of the property
Constraints
Constraints are modeled as options too, for example:
- default: The default value of the property
- required: Indicate if the property is required
- pattern: A regular expression pattern that a string should match
- min/max: The minimal and maximal value
- length: The maximal length of a string
Conversion and formatting
Format conversions can also be declared as options, for example:
- trim: Trim the string
- lowercase: Convert the string to be lowercase
- uppercase: Convert the string to be uppercase
- format: Format a Date
Mapping
Data source specific mappings can be added to the property options, for example, to map a property to be a column in Oracle database table, you can use the following syntax:
"oracle": {"column": "FIRST_NAME", "type": "VARCHAR", "length": 32}
Relations between models
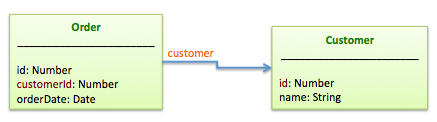
belongsTo
A belongsTo relation sets up a one-to-one connection with another model, such
that each instance of the declaring model "belongs to" one instance of the other
model. For example, if your application includes customers and orders, and each order
can be placed by exactly one customer.
var Order = ds.createModel('Order', {
customerId: Number,
orderDate: Date
});
var Customer = ds.createModel('Customer', {
name: String
});
Order.belongsTo(Customer);
The code above basically says Order has a reference called customer to User using
the customerId property of Order as the foreign key. Now we can access the customer
in one of the following styles:
order.customer(callback); // Get the customer for the order
order.customer(); // Get the customer for the order synchronously
order.customer(customer); // Set the customer for the order
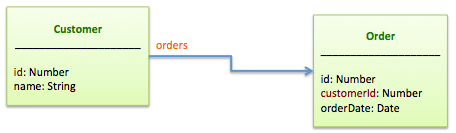
hasMany
A hasMany relation builds a one-to-many connection with another model. You'll
often find this relation on the "other side" of a belongsTo relation. This
relation indicates that each instance of the model has zero or more instances
of another model. For example, in an application containing customers and orders, a
customer has zero or more orders.
var Order = ds.createModel('Order', {
customerId: Number,
orderDate: Date
});
var Customer = ds.createModel('Customer', {
name: String
});
Customer.hasMany(Order, {as: 'orders', foreignKey: 'customerId'});
Scope methods created on the base model by hasMany allows to build, create and query instances of other class. For example,
customer.orders(filter, callback); // Find orders for the customer
customer.orders.build(data); // Build a new order
customer.orders.create(data, callback); // Create a new order for the customer
customer.orders.destroyAll(callback); // Remove all orders for the customer
customer.orders.findById(orderId, callback); // Find an order by id
customer.orders.destroy(orderId, callback); // Delete and order by id
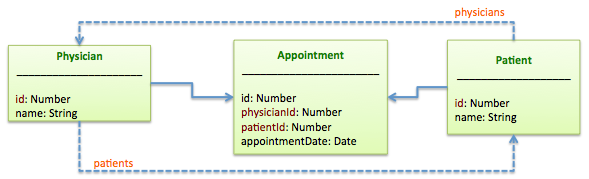
hasMany through
A hasMany through relation is often used to set up a many-to-many connection with another model. This relation
indicates that the declaring model can be matched with zero or more instances of another model by proceeding through
a third model. For example, consider a medical practice where patients make appointments to see physicians. The
relevant association declarations could look like this:
var Physician = ds.createModel('Physician', {name: String});
var Patient = ds.createModel('Patient', {name: String});
var Appointment = ds.createModel('Appointment', {
physicianId: Number,
patientId: Number,
appointmentDate: Date
});
Appointment.belongsTo(Patient);
Appointment.belongsTo(Physician);
Physician.hasMany(Patient, {through: Appointment});
Patient.hasMany(Physician, {through: Appointment});
Now the Physician model has a virtual property called patients:
physician.patients(filter, callback); // Find patients for the physician
physician.patients.build(data); // Build a new patient
physician.patients.create(data, callback); // Create a new patient for the physician
physician.patients.destroyAll(callback); // Remove all patients for the physician
physician.patients.add(patient, callback); // Add an patient to the physician
physician.patients.remove(patient, callback); // Remove an patient from the physician
physician.patients.findById(patientId, callback); // Find an patient by id
hasAndBelongsToMany
A hasAndBelongsToMany relation creates a direct many-to-many connection with
another model, with no intervening model. For example, if your application
includes users and groups, with each group having many users and each user
appearing in many groups, you could declare the models this way,
User.hasAndBelongsToMany('groups', {model: Group, foreignKey: 'groupId'});
user.groups(callback); // get groups of the user
user.groups.create(data, callback); // create a new group and connect it with the user
user.groups.add(group, callback); // connect an existing group with the user
user.groups.remove(group, callback); // remove the user from the group
Extend from a base model
LDL allows a new model to extend from an existing model. For example, Customer can extend from User as follows. The Customer model will inherit properties and methods from the User model.
var Customer = User.extend('customer', {
accountId: String,
vip: Boolean
});
Mix in model definitions
Some models share the common set of properties and logic around. LDL allows a model to mix in one or more other models. For example,
var TimeStamp = modelBuilder.define('TimeStamp', {created: Date, modified: Date});
var Group = modelBuilder.define('Group', {groups: [String]});
User.mixin(Group, TimeStamp);